

In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL SELECT INTO statement to create a new table from the result set of a query.
POSTGRESQL INSERT INTO SELECT CODE
The following shows the data from the short_film table: SELECT * FROM short_film Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) Title Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) The following statement creates a temporary table named short_film that contains the films whose lengths are under 60 minutes. To verify the table creation, you can query data from the film_r table: SELECT * FROM film_r Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) The PostgreSQL INSERT statement allows you to insert a new row into a table. Rating = 'R' AND rental_duration = 5 ORDER BY The following statement creates a new table called film_r that contains films with the rating R and rental duration 5 days from the film table.
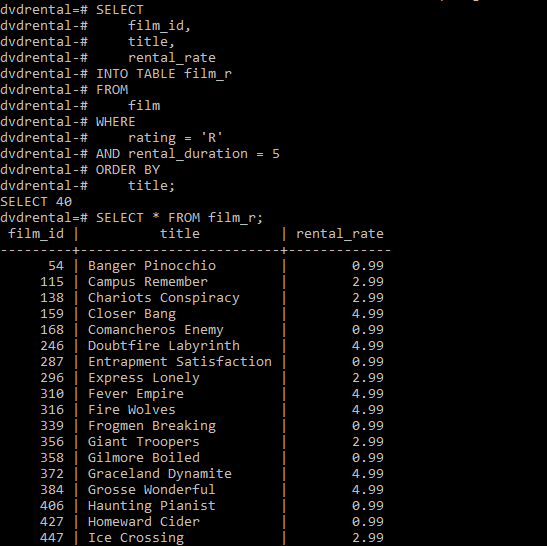
We will use the film table from the sample database for the demonstration. In this case, you can use the CREATE TABLE AS statement which provides more functionality than the SELECT INTO statement. Note that you cannot use the SELECT INTO statement in PL/pgSQL because it interprets the INTO clause differently. Besides the WHERE clause, you can use other clauses in the SELECT statement for the SELECT INTO statement such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, GROUP BY, and HAVING. The WHERE clause allows you to specify the rows from the original tables that should be inserted into the new table. The UNLOGGED keyword if available will make the new table as an unlogged table. The TEMP or TEMPORARY keyword is optional it allows you to create a temporary table instead. To create a new table with the structure and data derived from a result set, you specify the new table name after the INTO keyword. INTO new_table_nameĬode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) The following illustrates the syntax of the PostgreSQL SELECT INTO statement: SELECT Unlike a regular SELECT statement, the SELECT INTO statement does not return a result to the client. The new table will have columns with the names the same as columns of the result set of the query. The PostgreSQL SELECT INTO statement creates a new table and inserts data returned from a query into the table. Introduction to PostgreSQL SELECT INTO statement

If you are looking for the way to select data into variables, check it out the PL/pgSQL SELECT INTO statement. where d.Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL SELECT INTO statement to create a new table from the result set of a query. Where d.clmn3=customer_no - this is slower takes 3 to 4 min Join dib.tbl6 d on d.base_model = bm.base_model_code Join dib.tbl5 bm on dtc.device_type = bm.device_type Join dib.tbl4 rpm on rpm.profile_id=dtm.profile_id Join dib.tbl3 dtc on dtm.device_type_id = dtc.id So, is there a way to optimize the query to execute faster when passing parameter in where clause? CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION fn1(plan_id integer,customer_no text)įrom dib.tbl1 dtm join dib.tbl2 dtpmst on dtm.profile_id = dtpmst.profile_id I see a huge execution time difference varying from 1 sec to 4 min by passing the value and parameter in where clause respectively.Īnd obviously I have to use parameter in real time scenario. I have written a function(with parameters) to insert into a table from a select query with multiple joins and a where clause that will take input from parameter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
